Cascading plants are types of plants with a specific growth habit producing multiple canes that flow down to create a beautiful waterfall effect. Cascading plants, also known as trailers or spillers, naturally grow on the ground, but when given some elevation, they create gorgeous jungle-like coverage on retaining walls.
These plants are used in architecture to cover the facade of a building with lush greens or placed in hanging baskets in gardens, terraces, or balconies. Numerous types of cascading plants exist, including flowering plants, greenery, and even fruit-bearing plants.
Below is a list of the best cascading plants.
English Ivy
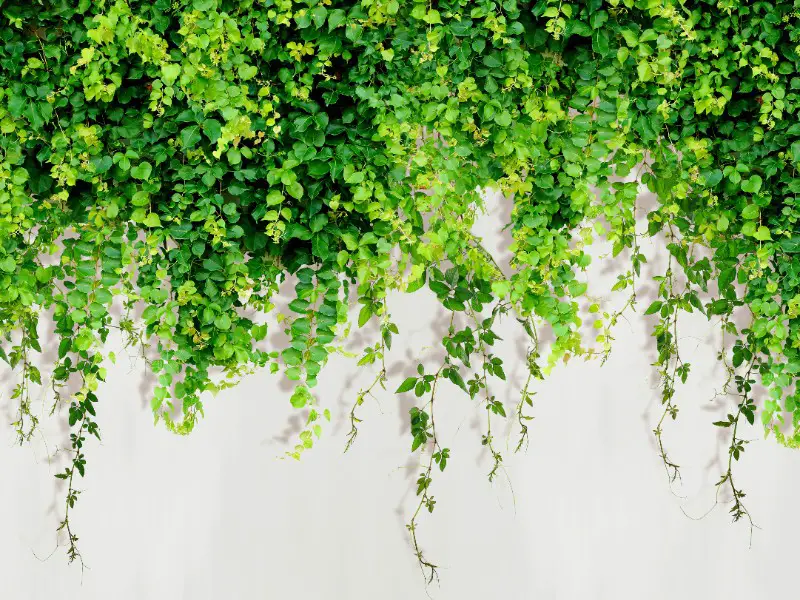

The English Ivy (Hedera helix) is a species of evergreen vine plant native to Europe and western Asia. This plant is recognizable by its thick, dark green leaves with three to five lobes when young that become lobeless when the plant matures. When blooming, the ivy produces small, white flowers.
The English ivy grows in zones 4 to 9, in part shade or even full shade, and prefers moist and fertile soils. Growing English ivy outside under a hardy tree like the Japanese umbrella pine provides perfect conditions for the plant’s quick growth. If grown inside, the ivy will need some indirect sunlight to develop and can be placed near a window or on a shaded balcony or terrace.
The English ivy vine blooms in the fall, producing tiny green and white flowers that may be unnoticeable under its thick leaves. The plant grows very quickly and can grow several feet in both height and width in a year. As English ivy is a climbing plant, it can climb up to almost 100 feet.
Dichondra (Silver Falls)
Dichondra (Dichondra argentea) — also called silver falls — is a beautiful evergreen, cascading plant known for its delicate silver-green leaves. It has small rounded leaves reminiscent of a water lily shape.
Dichondra plants thrive in zones 8 to 10, in warm and sunny climates. The plant is native to southern states and Latin American countries, like Mexico. It prefers sandy soils and can easily survive heat and short periods of drought, recovering quickly from withering when watered. Water these plants weekly to ensure steady growth.
The Dichondra blossoms in the late spring and early summer, but its small, yellow flowers are not particularly noticeable among its rich, silver leaves. The plant grows up to 4 inches in height and over 3-4 feet wide. Plant Dichondras 5 inches apart to ensure rich coverage over time.
Speckled Spur Flower
The speckled spur flower (Plectranthus ciliatus) is a unique evergreen ground cover plant that provides a wonderful cascading effect. The plant gets the name from its rich-purple leaves covered with purple fuzz. It has harmonious oval leaves with beautiful ornamentation.
The speckled spur flower is a species of tropical plant native to Africa. It prefers sandy soil and warm climates, but does not do well under direct sunlight, making it perfect to grow in zones 9 to 11. Grow speckled spur flowers in shady areas or, if kept indoors, avoid placing the plant near sunny windows.
The blooming season for the speckled spur flower is late summer and early autumn, during which it develops small, white flowers that are not as impressive as the leaves of the plant. Speckled spur flowers can grow up to 20 inches in height.
Sweet Potato Vine
The sweet potato vine (Ipomoea batatas) is a bright-green ornamental vine plant, popular among gardeners who place it in accent containers or use the plant as ground cover. The plant has characteristic greenish-yellow pointed leaves and develops insignificant flowers during the blooming season.
The sweet potato vine plant is native to South American tropical regions. It’s best suited for zones between 9 and 11. The sweet potato vine thrives in full sun and needs at least 6 hours a day for proper development. It does not tolerate frost, which may cause significant damage to the sweet potato vine. The best type of soil for this cascading plant is well-drained, moist, and enhanced with organic matter.
The sweet potato vine produces lush foliage, and blooms in spring or summer. The plant does not usually produce flowers, but when it does, they tend to be small and colored purple or pink. The sweet potato vine is an active grower, reaching up to 10 feet in width.
Golden Creeping Jenny
The golden creeping Jenny (Lysimachia nummularia) is one of the best cascading plants because of the unique bright-yellow color of its leaves. It has small, rounded leaves, creating delicate trailing patterns wherever it’s planted.
The golden creeping Jenny cascading plant grows best in zones 3 to 9. It enjoys partial shade, especially in the warmer regions during the afternoon hours. The perfect soil for this plant is either sandy or contains clay, providing proper filtration. The golden creeping Jenny needs lots of water to grow, so make sure to water it regularly and don’t allow the soil around it to dry out.
The golden creeping Jenny blooms in the summer, producing small yellow flowers. In fertile soil, golden creeping Jenny can grow up to 30 feet wide.
Glory Flower

The glory flower (Eccremocarpus scaber) is an evergreen vine plant recognizable by its elongated, dark-green, thick leaves and colorful tubular red, orange, and yellow flowers of around 1 inch in length.
Also known as the Chilean glory flower, the glory flower plant is considered tropical, so the best zones for this cascading plant are 8 to 10. The glory flower should be grown in fertile, neutral, and well-drained soil. The flower enjoys sunlight and can be kept in sunny spots in your garden or on an open balcony. In the spring and summer, water the plant generously when the soil dries up.
The glory flower blooms in late spring and early summer, developing colorful flowers that last until late autumn. It can crawl up to 14 feet in height and reach up to 3 feet in width.
Ivy Geranium
The ivy geranium (Perlargonium peltatum) is a popular flowering plant used in picturesque gardens to decorate hanging baskets and boxes, or left to trail freely across building walls. It has characteristic purple, pink, and white flowers which make the ivy geranium loved by many gardeners across the world.
The best zones to grow ivy geranium are 9 and 10. It enjoys lots of sunlight and thrives in bright daylight. However, when the outdoor temperature is above 80°F, provide the plant with some shade. The ivy geranium should be kept in well-drained soils, with regular watering to keep the soil moist necessary for proper development.
The ivy geranium plant blooms throughout the season. It flowers the most in colder climates and benefits from withered flowers being regularly cut. In maturity, ivy geranium can reach up to 3 feet in width.
Verbena
The verbena (Verbena peruviana), characterized by its beautiful flowering patterns of various colors, is one of many verbena varieties. Verbenas look great in gardens and can be grown on the ground or in containers to add color to garden spaces.
The verbena plant is native to South America and Asia but is very popular across the world. The best zones for verbena are between 8 and 11. The verbena enjoys sunny days and requires 6 to 8 hours of sunlight per day, and thrives in well-drained soils. Do not overwater verbenas, since these are delicate plants that might not recover from overwatering. Water your verbena if you see its leaves start to drop down a little.
The verbena blooms in late spring through to early fall. It maintains its bright flowers all season round. The mature verbena plant can reach up to 3 feet in height. Keep in mind that because these flowering plants spend so much energy blooming, they do not live very long. Plan on replacing verbenas every 2 to 3 years.
Creeping Phlox
The creeping phlox (Phlox stolonifera) is a stunning evergreen trailing plant with an abundance of pale purple and pink tiny flowers. This plant is used by gardeners to create a dense ground cover or grown to cover building walls.
The creeping phlox is native to the eastern parts of the United States and Canada. The best zones for this cascading plant are 3 to 9. The creeping phlox enjoys full sun in cooler climates but will need partial shade in hotter climates. While it handles both heat and frost well, prolonged periods of temperatures below 40°F can be harmful to it. This plant prefers fertile and well-drained soils, such as loamy soils. In the summer, water the creeping phlox weekly during periods without rain.
The creeping phlox blooms in the early spring, producing small tubular flowers of a variety of colors. The most common flower color is pale blue and purple, but pink, white, and even red flowers can also appear. The creeping phlox grows up to 6 inches tall and can reach up to 2 feet in width.
Creeping Thyme
The creeping thyme (Thymus praecox) is a small evergreen flowering plant commonly used as a lawn substitute by gardeners to create a lively, colorful ground cover. The creeping thyme is recognized by its small purple and pink flowers. An herb, creeping thyme has a pleasant scent and can even be used in cooking.
The creeping thyme plant grows best in zones 4 to 9, as it is native to the Mediterranean countries and enjoys full sun. The creeping thyme also grows well in infertile, poor soils. The key element of the soil is drainage, so the soil needs to contain rocks, sand, and loam. The plant also needs a lot of water, especially when young. In hot, rainless climates, make sure to water creeping thyme once a day. In cooler climates, water every week.
Creeping thyme blooms in early spring or summer and keeps its flowers for several weeks. The creeping thyme is a relatively slow grower, but it will start developing quicker once it adapts to the soil and watering regime. It can grow up to 6 inches tall and around 18 inches wide.
Cascading Rose
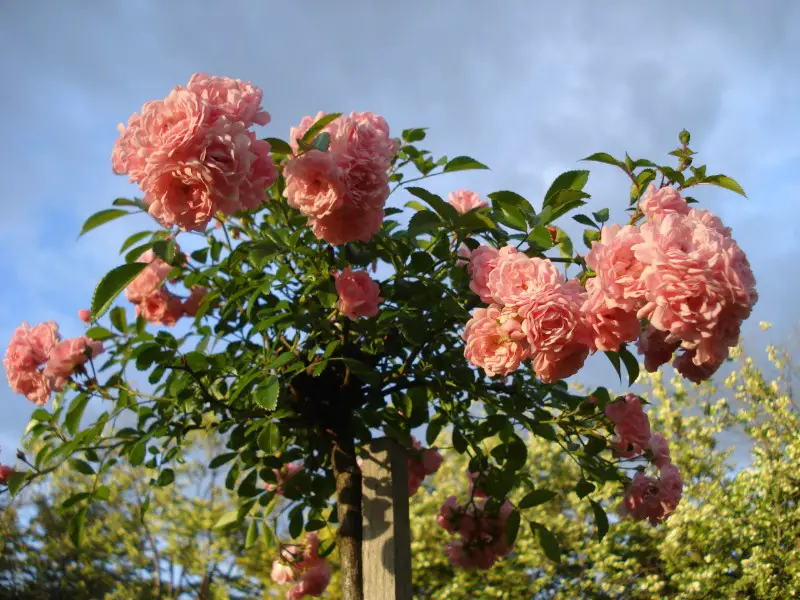

The cascading rose (Rosa), also known as red cascade, is a beautiful evergreen climbing plant that will become the center of attention in any garden. This plant has recognizable bright-red miniature rose flowers and bright-green leaves. It can be grown in small containers or used as a ground cover.
The cascading rose plant is native to Asia. It grows well in zones 4 to 9. It requires full sun exposure, around 6 hours a day, to help flowers develop. The cascading rose grows best in well-drained soils, which can be sandy or loamy. Make sure to water roses and thornless roses regularly, preferably in the mornings.
The cascading rose blooms in late spring and flowers throughout the entire season. The flowers are small, reaching about 1 inch in width. The plant can reach up to 12 inches in height and 5 feet in width.








Would be wonderful if you could include some photos. Great list!
This article is /2 assed at best.
I know little of plants, but I can write an article better than that without the least amount of effort. Which is what was used in this article.
1) show photos. This isn’t glossy photo expensive. Your phone probably does it.
F for effort.
2) when you show Glory flowers, you describe them. as red, yellow & orange. Then you show a photo (finally) and it’s violet.
Your article isn’t worth my time.
But if your publisher needs an editor, and they do…email me.
Other than the job pitch this is a total waste of air.
Cascading plants add beauty and softness to retaining walls, blending them seamlessly into the landscape. What are some types of cascading plants that thrive in various climates and soil conditions?